Unit 4
In unit 4 we learned about geometry. In this unit we studied geometry using graph papers to draw the figures.
In chapter 8 we were learning about coordinates. Using graph papers, we determined the point and location of a point.
*The image below is a coordinate plane that we use to determine a point, location, and coordinate.

To find the coordinate we need to order it by X then Y (x,y). After we get the coordinates we name it with a capital letter.
In chapter 10 we were learning about reasoning in geometry. So every answer that we put must be with reason. We were thought about alternate angle (Z-Angle), co-interior (C-Angle), and corresponding angle (F-Angle).
There are some terminologies in geometry:
Terminologies in geometry
- Point
- The basic element of geometric figure
- all geometric figure are made up of points
- use upper case letter
- no length and no width
- Line
- The connection between two or more points
- No endpoints
- Use lowercase letter
- Line segment
- Part of line with endpoint
- It has two endpoints
- use uppercase letter
- Identified by points at the end
- Ray
- Part of line with endpoint
- has 1 endpoint
- can be name by saying the endpoint first
- Use lowercase letter
- Collinear points
- Points that lie in a straight line
- Angle
- When two line meet each other in 1 point
An alternate angle is when a pair of parallel lines are cross by a transversal line and the angles (the blue angles in the picture) are equal.
a co-interior angle is when a pair of parallel lines are cross by a transversal line and form angles (as shown in the picture) where the sum of angles red area is 180 degrees.
Corresponding angles are when two parallel lines are crossed by a transversal line and form angles that are equal to the other as shown in the picture:
Worked example:
Not only that, we also learned about types of angles like opposite, complimentary, supplementary, obtuse, acute, etc. angles.
Opposite angle
Opposite angles are angles that are opposite. Both angles were made with the same two lines and is always equal.
Opposite angle:
The angle b and a are equal.
Complimentary angle
Complimentary angles are angles that add up to a total of 900.
Example:
Supplementary angle
Supplementary angles are angles that add up to a total of 180o.
Example:
Obtuse angle
Obtuse angles are angles that are more than 90o.
Examples:
Acute angle
Acute angles are angles that less than 90o.
Examples:
Circle
- Parts of circle
A=
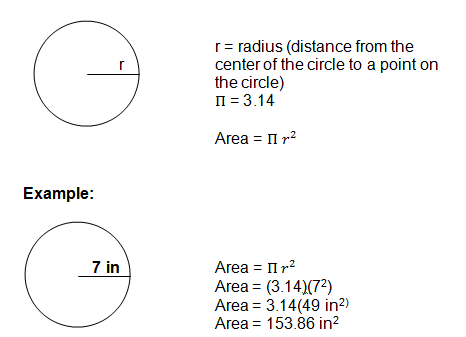
So we need to multiply the diameter of the circle with the pi












No comments:
Post a Comment